With the wide application of stainless steel flanges in our society, the demand for flanges in the market is gradually increasing, we know that flanges are more used in welding pipes, we have professional personnel to see its use to express their views
Use of stainless steel flange
Stainless steel flanges In pipeline engineering, flange are suitable for pipe connection. In the need to connect the pipe, a flange is installed, low pressure pipe can use wire flange, more than 4 kg of pressure using welded flange.
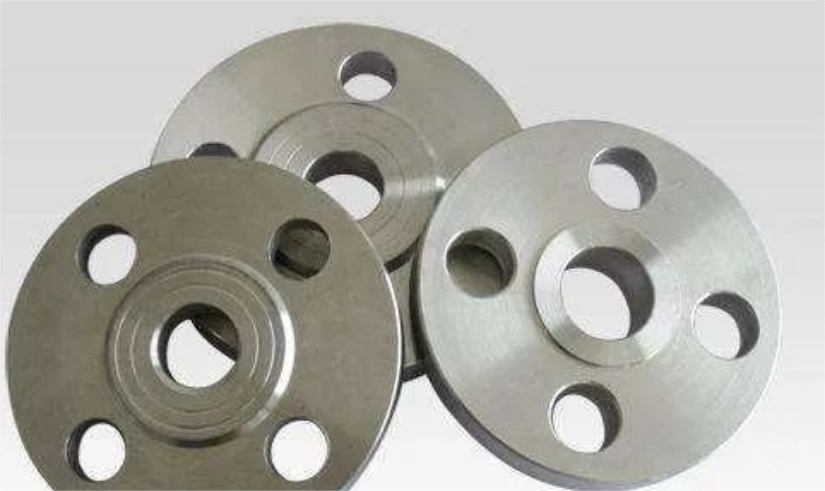

A gasket is placed between the two flanges and then bolted. Different pressure flanges have different thicknesses using different bolts.
In the welding process of stainless steel flanges, carbides will be precipitated by repeated heating, and the refracted carbides will also reduce corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Therefore, when welding stainless steel flanges, repeated heating can not be carried out to avoid reflecting carbides affecting the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of stainless steel flanges.
How to judge the authenticity of stainless steel flange
A notable feature of stainless steel flanges is their inherent corrosion resistance to concentrated and dilute nitric acid. This property makes it relatively easy to distinguish most of the remaining metals or alloys. As everyone knows, high-carbon 420 and 440 steel is slightly etched in the nitric acid test, and non-ferrous metals will be etched immediately when they encounter concentrated nitric acid. Dilute nitric acid is highly corrosive to carbon steel.

Magnetic test is the most effective way to distinguish annealed austenitic stainless steel from ferritic stainless steel. Austenitic stainless steel is non-magnetic steel, but it has slight magnetic properties after cooling at high pressure. Pure chromium steel and low alloy steel are strong magnetic steels.
Copper sulfate point test is the most effective way to quickly distinguish ordinary carbon steel and various stainless steel. The concentration of copper sulfate solution is 5~10%. Before point inspection, the test area should be quickly cleaned of grease or various impurities, grind the small plate with a soft cloth, and then drop the copper sulfate solution into the clean plate. Ordinary carbon steel or iron forms a layer of metallic copper in a few seconds, while stainless steel surfaces do not produce copper precipitation or display copper color.
Stainless steel flange inspection can distinguish 302 and 304 from 316 and 317. The cutting edge of the sample should be finely ground, and then cleaned and passivated for half an hour in nitric acid with a volume concentration of 20~30% and a temperature of 60~66℃.

The sulfuric acid test solution is heated to 71℃ with a volume concentration of 10%. When.302 and 304 steels are immersed in this hot solution, they will be rapidly etched and produce a large number of bubbles, and the samples will turn black in a short time
The samples of 316 and 317 steel are not etched or slow in chemical reaction, and the samples do not fade in 10 to 15 minutes. The test can be more accurate if similar comparisons are made by simultaneously examining samples with known components.